Compilation and translation: Saeed Mahmoud Kalaye, Mohammad Gholamnejad, Hamid Mahmoud Kalaye
TCNA
Ceramic Tile Association of North America; An organization formed by North American tile and ceramic manufacturers that provides services for the development of knowledge related to the tile industry, specifically installation knowledge. This organization has prepared a booklet as an installation guide, which is based on American standards regarding materials and their installation. Today, with the development of this institution throughout North America, the aforementioned instruction, which was first published in 1954, has been reprinted many times and is cited throughout this country as the basis of work.
Template
pattern, template; A pattern for repetitive designs or a stone processing and preparation process.
Terrazzo
marble concrete, marble mosaic (in-situ mosaic); The flooring is created by using a combination of granite and marble pebbles on a cement or resin base and its surface is polished after the work is finished.

Texture
Texture; The modified appearance of building stone by one or more mechanical operations
Textured Finish
textured finish; Any stone finish that makes its surface uneven due to aesthetic reasons or resistance to sliding in the direction of pedestrians.
Thermal Finish
Thermal finishing (flame); A type of polishing in which the surface of the stone is exposed to high heat for a short period of time.
Thin Stone
thin facade stone; A stone whose thickness is less than 50 mm.
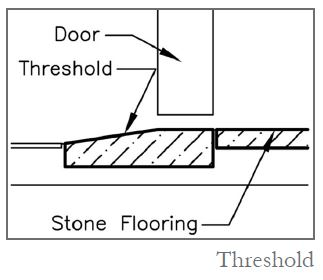
Threshold
door threshold; A flat stone beam or worn tool that is placed at the foot of the entrance door and its upper surface is seen at the level of the ground. One of its uses is to differentiate between two adjacent spaces.
Tile
stone tile, stone mosaic; A thin and regular piece of stone (in terms of dimensions and pattern) with a thickness of less than 20 mm, whose dimensions will be 60 mm in most cases.
Tilt Shop Cart
Wheelbarrow carrying stone; A device used to move stone in a factory, or cut pieces in a shop. These devices have a kind of bottom whose angle changes to some extent and in this way they are able to move the stones vertically.
Tin Oxide
tin oxide; A powder that is used for polishing the surface of granite and looks like talc. These materials are applied to the surface of the stone using a felt plate and the polishing is done.
Tolerance
tolerance limit; The permissible limit for being different from the specified dimensions.
Tooled Finish
Engraved stone facade; A type of finish that usually creates 4, 6 or 8 concave and parallel grooves on the surface of the stone at 25 mm intervals.
Translucence
semi-transparent, semi-transparent; One of the characteristics of some light-colored marbles and some light-colored marbles is that they allow light to pass through them.
Travertine
travertine; A type of porous limestone that is among decorative stones. This stone is left over from the sediments of the mineral waters of caves or hot springs or from the sediments of the bottom of the seas and rivers, which are seen in relatively wide areas. Some types of travertine are commercially marketed as marble after polishing and polishing.
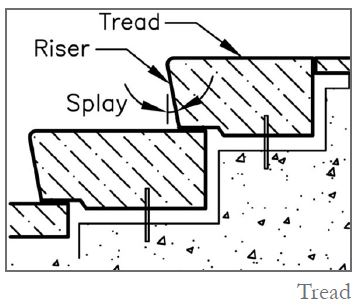
Tread
floor stone; A part of the stairs that is flat and smooth and traffic is carried out on it.
Trim
Zoar, framing; A kind of framing and edging for walls, openings or other similar elements in the interior and exterior of the building, which are executed in forms such as wall cornice, wall framing, wall lip and window frame.
Tumbled Finish
Polishing with rotary abrasive tools; A type of finish that makes the appearance of the stone similar to old stones and weathered erosion, and this is done through sand, pebbles and small metal balls that cause wear on the surface of the stone.
Ultimate Capacity
final capacity; The maximum load that a metal harness can withstand and applying more force will cause this part to break. This number must be divided by the safety factor in order to obtain the permitted capacity.
Undercut
cut from below; A kind of cut from the lower surface that leads to the subject being suspended in the upper part.
Unit
unit piece; A piece of building stone that has been polished and processed in the form of face stone or massive stone.
Urinal Screen
water separator plate; A thin stone plate installed as a partition wall between toilets.
Vacuum Cups
glass (stone) sucker; A tool for lifting and carrying thin and smooth stones that is similar to a cup and has a concave surface. In this device, the air suction by the device causes a strong connection between the stone and the device, and to prevent air leakage from the edges and to make the device safe, a sealing gasket is installed on its end edge.
Vacuum Lifter
space elevator; Any kind of device for moving stone that uses a cup-shaped tool and its required force is provided by creating a vacuum or suction.

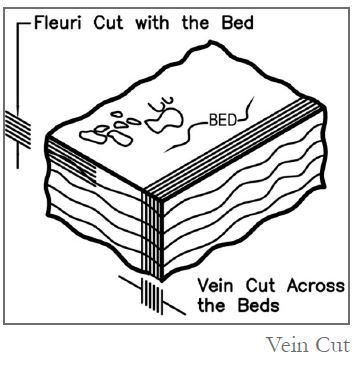
Vein Cut
vein cut; A kind of cut in stone blocks that is made perpendicular to the bed of stone formation and exposes the veins and layers of the stone.
Vein
vein, ore vein; An irregular and narrow layer, streak or element that contrasts with its surrounding materials in terms of color and texture or both.
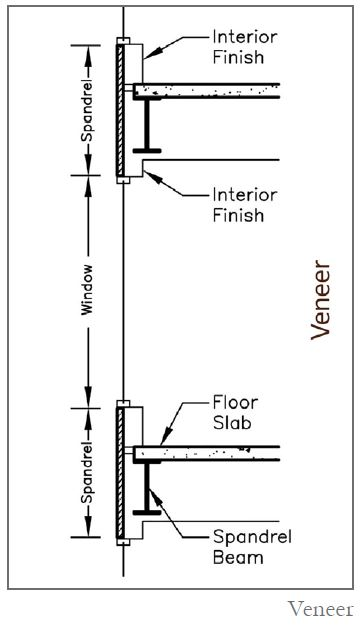
Veneer
stone facade, facing stone; A kind of stone that has a non-structural use and is used in the facade of the building for the purpose of decoration or protection of the lower layers.
Venting
ventilation port;
Vug
Kawiz, cavity; A natural cavity in a rock that may contain crystals or layers of minerals. It is often found in dolomite and limestone. This element can be formed as a result of the dissolution or recrystallization of minerals. The dimensions of these holes are not limited, but usually vary from a fraction of a centimeter to several centimeters. These cavities may be enclosed by layers of crystalline or cluster minerals.

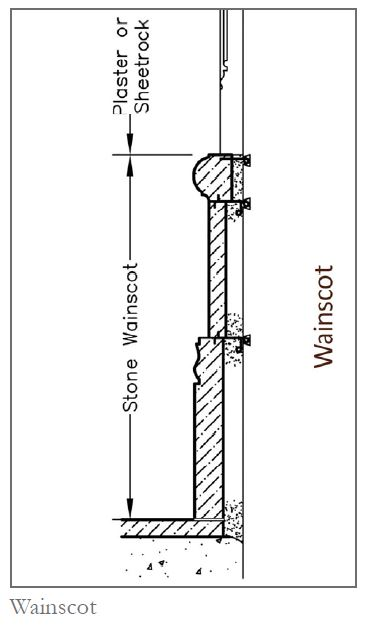
Wainscot
Rokob; A stone coating that is used in the interior to cover the lower parts of the walls.
Wall Tie
Masonry fasteners; In the term of masonry, it refers to a type of restraint, which is usually in the form of a metal belt, and it is used to create a secure connection between the front wall and the load-bearing wall in double-walled walls. These fasteners are placed in the mortar and are fixed during installation, and therefore, they do not need to create a groove, crotch, or tongue.
Walls, bearing
porter wall; A type of load-bearing wall that is able to withstand gravity forces in addition to its own weight.
Walls, cavity
double wall; A type of wall whose inner and outer walls are separated from each other and the air flows in this part, but they are connected with each other using fasteners.
Wash
roof gutter; The slope of the stone pieces that leads to rain water.

Water Jet
water cutting machine; A device that creates controlled cuts in the rock by directing water at a very high pressure through a tiny pore along with abrasive materials. The cutting lines in this method are very precise and thin, and complex shapes can be created on the stone with the help of this method and computer system.

Water Recycling System
water recycling system; Any type of water recycling system used in stone processing and preparation workshops that provides conditions where water can be reused by filtering or neutralizing the chemical properties of water.
Water Repellent
moisture insulation; A variety of chemical liquid compounds that are applied to the surface of the material and thereby reduce the amount of moisture absorption by the surface of the stone, but it is said that they do not completely prevent it from breathing. This issue differentiates these materials with coatings such as sealers that prevent materials from breathing.
Water Table
watering can A strip of material that protrudes from the surface of the wall and is usually executed at a level close to the ground (usually on the plinth) and its upper edge has a small chamfer and its lower surface also has a groove, thereby managing to repel rainwater. .
Water-jet Finish
Finishing with water cutting machine; A kind of polishing and improving the appearance of the stone surface that is done using water under high pressure.
Waterproofing
being waterproof;
Waxing
wax work, stone plastering; The process of filling small holes and spills and defects of the stone surface using liquid alcohol varnish, cabinet putty or special polyester compounds. In the construction stone industry, this process is different from the use of wax putty used in polishing the stone surface.
Wear
Clearing; Removing materials or disturbing factors from the stone surface using abrasive methods.
Weathering
weathering; Natural transformations of materials such as stone as a result of chemical and physical processes caused by atmospheric actions, soil, surface water, underground water or temperature changes are called weathering.
Wedging
with splitting wedge; The process of splitting rock using wedges in the place of weak layers of rock or the holes in it and finally applying compressive force to the wedges.
Weep Holes
The wall’s reputation, the sweat hole; Holes in the place of fastening the facade, or structural parts supporting the facade to allow moisture and rainwater to pass from the middle space of the wall to the outside of the building.

Wire Sawing
cutting with wire; This method is that they first dig two holes perpendicular to each other in the area of the desired block (the holes are connected to each other), then pass the steel wire through the holes and pull the wire to remove the stone in the mentioned place. This movement creates a groove in the stone, and an abrasive material such as quartz and water is poured into the created groove to reduce the cutting of the stone, which is usually less hard than quartz. Today, the term is mainly applied to the cutting process with cables equipped with diamond abrasive elements (at regular intervals) that are cooled using water.

Wythe
جدار، تیغه؛ قسمت داخلی یا خارجی یک دیوار دوجداره را جدار یا تیغه مینامند.
